How Liquid Waste Disposal Functions: A Comprehensive Summary of Methods and Technologies Used

Summary of Fluid Waste Types
The complexity of liquid waste types requires a detailed understanding of their attributes and ramifications for disposal. Fluid waste can generally be categorized into a number of kinds, including industrial, community, farming, and harmful waste. Each category shows unique properties, requiring certain administration approaches to reduce environmental and health and wellness risks.
Industrial liquid waste stems from manufacturing processes and usually has an array of pollutants, such as hefty steels, solvents, and natural substances. Municipal fluid waste, mostly comprising wastewater from families and business establishments, includes raw material, nutrients, and virus (industrial wastewater treatment). Agricultural liquid waste, consisting of drainage from ranches, may have plant foods, pesticides, and pet waste, presenting threats to water high quality and communities
Dangerous liquid waste is characterized by its poisoning, sensitivity, or potential to create harm. This category includes materials like acids, bases, and specific chemicals that necessitate stringent handling and disposal procedures. Understanding these varied liquid waste types is vital for developing reliable disposal methods and making sure conformity with environmental laws. Correct category and characterization are essential for implementing suitable treatment techniques and reducing the damaging influence on public health and the setting.
Physical Treatment Methods

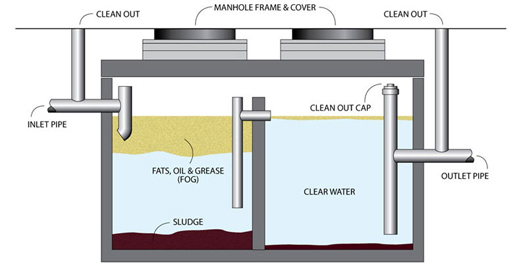
Screening is the preliminary step, where larger particles and particles are removed from the liquid waste utilizing screens or grates. In sedimentation storage tanks, much heavier fragments settle at the base, creating a sludge layer, while the cleared up liquid can be more treated.
Filtration is another crucial technique that involves passing the fluid through permeable products, such as sand or membranes, to record smaller fragments. This action boosts the top quality of the liquid, making it suitable for subsequent therapy processes.
Chemical Therapy Methods
Chemical treatment methods are crucial for effectively taking care of liquid waste, particularly in dealing with liquified and colloidal impurities that physical methods may not adequately eliminate. These techniques make use of different chemical representatives to reduce the effects of, precipitate, or transform unsafe substances into less hazardous forms.
One usual method is coagulation and flocculation, where chemicals such as alum or ferric chloride are contributed to advertise the gathering of suspended fragments. This procedure enhances sedimentation, permitting much easier removal of the resulting sludge. Furthermore, oxidation processes, employing representatives like chlorine or ozone, are utilized to break down intricate natural compounds and virus, providing the waste more secure for discharge or additional treatment.
Neutralization is an additional crucial strategy, which readjusts the pH of acidic or alkaline waste streams to neutral levels, preventing possible harm to downstream systems and the setting. Moreover, progressed oxidation procedures (AOPs) utilize mixes of oxidants and ultraviolet light to degrade consistent contaminants, achieving a greater level of treatment performance.
Biological Treatment Processes
Biological treatment procedures play a crucial duty in the management of liquid waste by making use of microorganisms to disintegrate raw material and minimize contaminant levels. These processes can be broadly classified into anaerobic and cardiovascular therapies, each utilizing particular microbial areas to accomplish reliable waste destruction.
Aerobic therapy involves the usage of oxygen to promote the failure of organic products by germs. This process is generally carried out in triggered sludge systems, where aeration containers supply a conducive atmosphere for microbial growth, resulting in the oxidation of natural contaminants. The resultant biomass can be divided from treated effluent with sedimentation.
In contrast, anaerobic therapy occurs in the absence of oxygen, depending on different microorganisms to this website damage down natural issue. This approach is specifically advantageous for high-strength waste, as it produces biogas, a sustainable energy source, while reducing sludge manufacturing. Technologies such as anaerobic digesters are regularly utilized in commercial and community applications.
Both cardiovascular and anaerobic biological treatments not only decrease the ecological influence of liquid waste but likewise facilitate source recovery, making them crucial parts of lasting waste monitoring methods. Their performance, efficiency, and versatility support their widespread execution throughout various sectors.
Emerging Technologies in Disposal
Cutting-edge techniques to liquid waste disposal are quickly developing, driven by advancements in innovation and an increasing focus on sustainability. Amongst these arising modern technologies, membrane layer bioreactors (MBRs) have actually gotten grip for their ability to combine biological therapy with membrane layer purification, leading to top notch effluent that can be reused in various applications. MBRs enable smaller sized footprints and a lot more effective procedures compared to standard systems.
Another appealing development is making use of anaerobic digestion combined with nutrient recuperation modern technologies, which not just deals with fluid waste yet likewise creates biogas and dig this recuperates beneficial nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus. This twin advantage enhances resource performance and lowers ecological impact.
In addition, progressed oxidation procedures (AOPs) are being adopted for the destruction of complicated organic contaminants. These techniques use powerful oxidants and catalysts to damage down pollutants at the molecular level, providing a very efficient option for difficult waste streams.
Furthermore, the integration of expert system and artificial intelligence in waste monitoring systems is optimizing functional performance and predictive upkeep, leading to minimized expenses and improved environmental compliance. These modern technologies show a significant change in the direction of more efficient and lasting liquid garbage disposal methods.
Verdict
In final thought, reliable liquid waste disposal requires a thorough understanding of various methods and modern technologies. By continuously progressing these you can check here techniques, it becomes feasible to resolve the growing obstacles associated with liquid waste, inevitably contributing to ecological protection and source healing.
Fluid waste disposal is a crucial facet of environmental monitoring, requiring a thorough understanding of different techniques and modern technologies tailored to various waste types. Fluid waste can broadly be categorized right into numerous kinds, including industrial, community, agricultural, and harmful waste. Agricultural fluid waste, consisting of overflow from farms, may include fertilizers, pesticides, and animal waste, positioning dangers to water high quality and environments.
Different physical treatment techniques play an important function in handling liquid waste efficiently - industrial wastewater treatment.In final thought, effective fluid waste disposal demands a thorough understanding of numerous methods and innovations